Brain Surgery - Dr. Pravin Ganjre
There are numerous types of brain surgery. The type used is based on the area of the brain and the condition being treated. Advances in medical technology have enabled surgeons to operate on portions of the brain without a single incision in or near the head.
Brain surgery is a critical and complicated process. The type of brain surgery done depends highly on the condition being treated. For example, a brain aneurysm can be repaired using a catheter that’s introduced into an artery in the groin. If the aneurysm has ruptured, an open surgery called craniotomy may be used. Surgeons, while being as careful and thorough as possible, treat each surgery on a case-by-case basis.
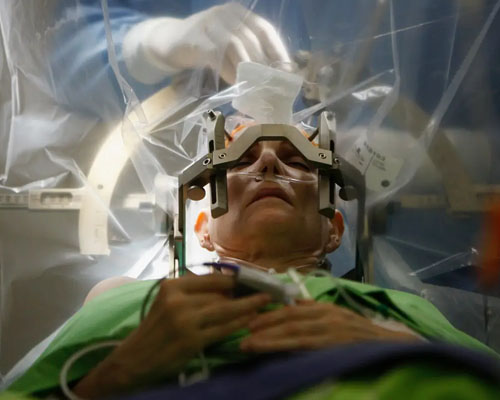
Brain surgery involves different procedures to repair the structural problems of the brain. Different types of brain surgeries are performed depending on the affected area and condition of the brain. Advanced technologies in the medical field allow brain surgeons to operate on any portion of the brain without an incision in or near the head.
Brain surgery is one of the most specialized and delicate branches in the field of medicine. Due to the of advances in the instrumentation and better-developed infrastructure, it is quite safe and has excellent results. These surgical procedures are no more prolonged operations and now we have far better anaesthetic agents available. Brain tumour means growth in the Brain or in the cranial compartment. These tumours can be completely excised. These tumours can occur in any part of the Brain and surgeons can reach all these tumours for its excision.
Blood clots can occur in the Brain and it requires immediate removal or evacuation by surgery which can be done on an emergency basis. The water content in the Brain can increase because of various reasons and shunt procedures are routinely done to overcome this problem, especially in children. Some children are born with abnormalities of the head and Brain, there are many corrective procedures which are necessary at that early age for a child’s normal growth.
The stereotactic procedures now are routinely performed, especially for small lesions of the Brain. The incision is very small and sometimes these procedures are done under local anaesthesia. In the case of head injuries, surgery is needed if there is a fractured skull, or blood clot in and around the brain. Recovery from anaesthesia is almost immediate, patients can eat and drink within a few hours after surgery. After brain surgery, the person needs a short stay in the hospital and within a few weeks can resume his /her job.
Treatment of Brain Tumour:
Surgery is the first and most common treatment for most patients with brain tumors. It is highly successful for most benign tumours. Surgery is usually the best treatment for tumors that neurosurgeons can reach without severely damaging normal brain tissue near the tumor.
Neurosurgeons can surgically remove some tumors completely (called resection or complete removal). If the tumor is near sensitive areas of the brain, neurosurgeons will only be able to remove part of it (called partial removal). Even partial removal can relieve symptoms and facilitate or increase the effectiveness of other treatments.
A biopsy is a surgical procedure to remove a small sample of a brain tumor for examination under a microscope — is usually performed during surgery to remove the tumor. This enables doctors to confirm the diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment. If the patient is not a surgical candidate, a separate biopsy may be done.
The role of surgery in treating brain tumours
Surgery can provide:
The complete removal of some brain tumors
• A sample to enable doctors to diagnosis the tumor and recommend the most appropriate treatment
• Better quality of life:
– Reduced symptoms and improved ability to function (e.g., to think, speak or see better)
– Less pressure within the skull from the tumor
• A longer life
Types of Brain Tumour Surgery
Surgery is one type of treatment for brain tumors. The most common types of surgery are:
• Biopsy
• Craniotomy
• Extended bifrontal craniotomy
• “Eyebrow” craniotomy (supra-orbital craniotomy)
• “Keyhole” craniotomy (retro-sigmoid craniotomy)
• Orbitozygomatic craniotomy
• Translabyrinthine craniotomy
• Endonasal endoscopy (endonasal endoscopic surgery)
• Neuroendoscopy
Types of brain surgery
- A craniotomy involves making an incision in the scalp and creating a hole known as a bone flap in the skull.
- Biopsy
- Minimally invasive endonasal endoscopic surgery.
- Minimally invasive neuro endoscopy.
- Deep brain stimulation
Possible risks of brain surgery are:
- Problems with speech, memory, muscle weakness, balance, vision, coordination, and other functions. These problems may last a short while or they may not go away.
- Blood clot or bleeding in the brain.
- Seizures
- Stroke
- Coma
- Infection in the brain, wound, or skull.
- Brain swelling
Most often, it’s not known why people without inherited syndromes develop brain or spinal cord tumours. Most exposures that cause cancer somehow damage DNA. … Other than radiation, no known lifestyle-related or environmental factors are clearly linked to brain tumours.
Grade I brain tumours may be cured if they are completely removed by surgery. Grade II — The tumour cells grow and spread more slowly than grade III and IV tumor cells. They may spread into nearby tissue and may recur (come back). … Grade IV tumours usually cannot be cured.
Possible risks associated with brain surgery include:
- allergic reaction to anaesthesia.
- bleeding in the brain.
- a blood clot.
- brain swelling.
- coma
- impaired speech, vision, coordination, or balance.
- infection in the brain or at the wound site.
- memory problems
